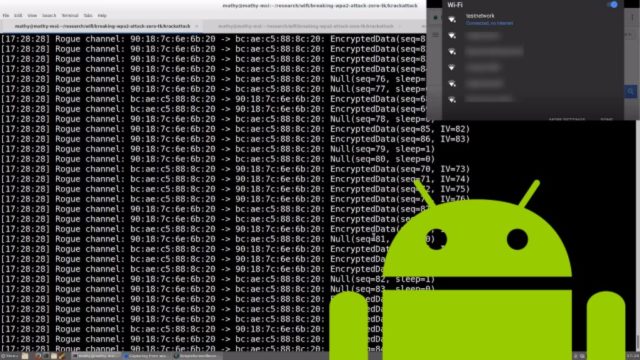
he website krackattacks.com is now live and provides details on the recently known WPA2 exploit proof-of-concept known as KRACK (Key Reinstallation Attack).
The KRACK attack works on all modern protected WiFi networks against both WPA1 and WPA2, and against cipher suites including WPA-TKIP, AES-CCMP, and GCMP). The list of products affected by some variant of attack includes Android, Linux, Apple, Windows, OpenBSD, MediaTek, Linksys, and more.
It can allow attackers to steal information such as credit cards, passwords, chat messages, email, photos, etc. An attacker might also be able to inject and manipulate data.
While almost every supported device and OS is at the risk of being attacked, it appears some operating systems could have far worse consequences, namely, Android and Linux. The wpa_supplicant is the WiFi client commonly used on Linux and Android (6.0 and above).
“Our attack is especially catastrophic against version 2.4 and above of wpa_supplicant, a Wi-Fi client commonly used on Linux,” wrote the researcher Mathy Vanhoef on the website. He found the vulnerabilities accidentally while he was working on another paper.
 Around 41% of Android devices are affected due to a devastating attack vector variant developed by the researcher which makes it “trivial to intercept and manipulate traffic sent by these Linux and Android devices.”
Around 41% of Android devices are affected due to a devastating attack vector variant developed by the researcher which makes it “trivial to intercept and manipulate traffic sent by these Linux and Android devices.”
 Around 41% of Android devices are affected due to a devastating attack vector variant developed by the researcher which makes it “trivial to intercept and manipulate traffic sent by these Linux and Android devices.”
Around 41% of Android devices are affected due to a devastating attack vector variant developed by the researcher which makes it “trivial to intercept and manipulate traffic sent by these Linux and Android devices.”
Sadly, we still don’t have WPA3, but any possible fix for the KRACK attack would be backward-compatible with previous WPA implementations. And contrary to what one might assume, changing passwords won’t do much better than satisfying oneself. Vanhoef suggests a more rigorous inspection of the security protocols to deal with such problems.
Various vendors were notified about the problem as early as July, so we might expect updates for end-user devices, if not networking hardware. In fact, according to Vanhoef, the access points and routers might not require security updates as their attack primarily targets clients.
For routers, he suggests disabling functionalities such as client mode and 802.11r (fast roaming). Home users advised to update their WiFi compatible devices including computers and smartphones.
You can read about KRACK attack in detail on the website.